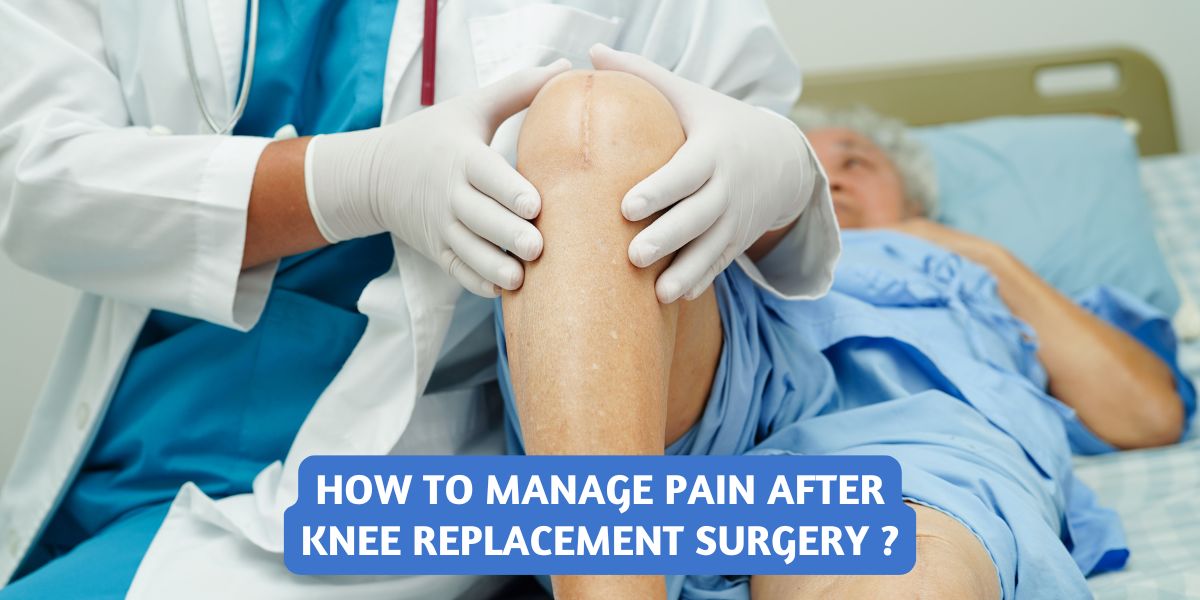
Knee replacement surgery is an important procedure designed to relieve pain and restore function in patients suffering from chronic knee pain due to arthritis or injury. However, pain management after surgery is critical to a successful recovery. Effective pain management can speed up recovery, reduce complications, and improve overall mobility. Here we outline the best practices for managing post-operative pain and ensuring a smoother recovery.
1. Understanding Post-Surgical Pain
After knee replacement surgery, it is normal to experience discomfort, swelling, and stiffness around the knee. Pain typically peaks 24 to 48 hours post-surgery and gradually decreases over the following weeks. Managing pain early and effectively is essential for a quicker return to everyday activities.
The types of pain commonly experienced after knee surgery include:
- Acute pain: Immediate post-surgical pain caused by tissue damage during surgery.
- Inflammatory pain: Swelling and inflammation in the surrounding tissue as the body heals.
- Referred pain: Discomfort in other areas such as the hips or lower back, often due to changes in posture and walking mechanics.
2. Pain Medication Management
Medication is the cornerstone of post-operative pain control. Doctors prescribe a combination of pain relievers to target different types of pain and ensure comprehensive relief. Common medications include:
- Opioids: Strong painkillers prescribed for short-term use immediately after surgery. These include medications like oxycodone or hydrocodone. Patients should follow their doctor’s instructions to avoid potential side effects like nausea, dizziness, and addiction.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These are often used alongside opioids to reduce inflammation and pain. Examples include ibuprofen and aspirin.
- Acetaminophen: A commonly prescribed medication to manage mild to moderate pain.
- Nerve blocks: In some cases, regional anesthesia or nerve blocks are administered during surgery to reduce post-operative pain for the first 24 to 48 hours.
It is important to use pain medications as prescribed and gradually wean off opioids to avoid dependency.
3. Cold Therapy and Compression
Cold therapy or cryotherapy involves the use of ice packs or cold compression systems applied to the knee. This helps reduce swelling, inflammation, and pain by numbing the surgical site. Applying cold therapy several times a day for 20 minutes at a time can significantly ease post-operative discomfort.
Compression wraps or devices also help control swelling by preventing excess fluid buildup. This can enhance comfort and accelerate healing.
4. Physical Therapy and Exercise
Rehabilitation exercises play a vital role in managing pain after knee replacement surgery. Movement and stretching help improve range of motion, prevent stiffness, and boost circulation in the knee joint. Early physical therapy is usually recommended within 24 hours of surgery.
Some of the exercises that are commonly suggested include:
- Ankle pumps and foot rotations: These exercises can help reduce swelling and increase blood circulation.
- Quadriceps sets: Tightening the muscles at the front of the thigh can help improve knee strength.
- Straight leg raises: Strengthening the muscles around the knee without bending the joint.
- Knee bends: Gradually improving knee flexibility.
Patients should follow their physical therapist’s guidance on how much activity to perform, ensuring that they do not overexert themselves and cause more pain or complications.
5. Proper Rest and Elevation
Rest is crucial for recovery. However, finding a balance between rest and activity is key. Too much inactivity can cause the knee to stiffen, while too much movement too soon can delay healing.
Elevation of the leg is another important aspect of managing post-operative swelling. Patients should keep their leg elevated, ideally above heart level, to reduce fluid retention and inflammation. This will decrease throbbing pain and pressure in the knee.
6. Diet and Hydration
A healthy diet plays a significant role in post-surgical recovery and pain management. Protein-rich foods aid in tissue repair, while anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, berries, and fatty fish can reduce inflammation and support healing.
Staying hydrated is equally important. Adequate water intake ensures that tissues remain lubricated and aids in reducing inflammation. It also supports the effectiveness of medication and promotes faster recovery.
7. Alternative Pain Relief Methods
Several alternative therapies can complement traditional pain management techniques:
- Massage therapy: Helps relax muscles around the knee and may relieve referred pain.
- Acupuncture: Involves inserting thin needles into specific pressure points to reduce pain.
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): A small device that sends electrical impulses to disrupt pain signals sent to the brain.
Patients should consult their healthcare providers before incorporating alternative therapies to ensure they are safe post-surgery.
8. Wound Care and Infection Prevention
Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection, which can exacerbate pain and delay healing. Patients should:
- Keep the surgical site clean and dry.
- Follow the surgeon’s guidelines for dressing changes.
- Watch for signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, or discharge from the wound.
Infections can cause severe pain and complications, so immediate medical attention is required if an infection is suspected.
9. Managing Long-Term Pain
While pain generally subsides within a few weeks, some patients may experience chronic pain for months after surgery. This can be due to a variety of factors, such as:
- Nerve irritation
- Scar tissue formation
- Underlying health conditions
Patients experiencing prolonged pain should consult their surgeon for a comprehensive evaluation and consider treatments like corticosteroid injections, nerve blocks, or further physical therapy.
10. Mental and Emotional Well-being
Surgery can take a toll on a patient’s mental health, and pain that is not relieved can lead to feelings of anxiety, depression, or frustration. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing and counselling can improve the emotional aspects of pain management.
Find the Best Knee Replacement Doctor in Pune
Effective pain management after knee replacement surgery involves a multi-faceted approach, including medications, cold therapy, physical therapy, and a healthy lifestyle. Adhering to a structured recovery plan not only minimizes pain but also helps patients regain mobility and return to normal activities faster. Always follow your surgeon’s advice and report any unusual or persistent pain to ensure a smooth recovery process. Consult Dr. Murtaza Adeed is One of the best knee replacement surgeon in Pune, Maharashtra.